What is a meningioma?
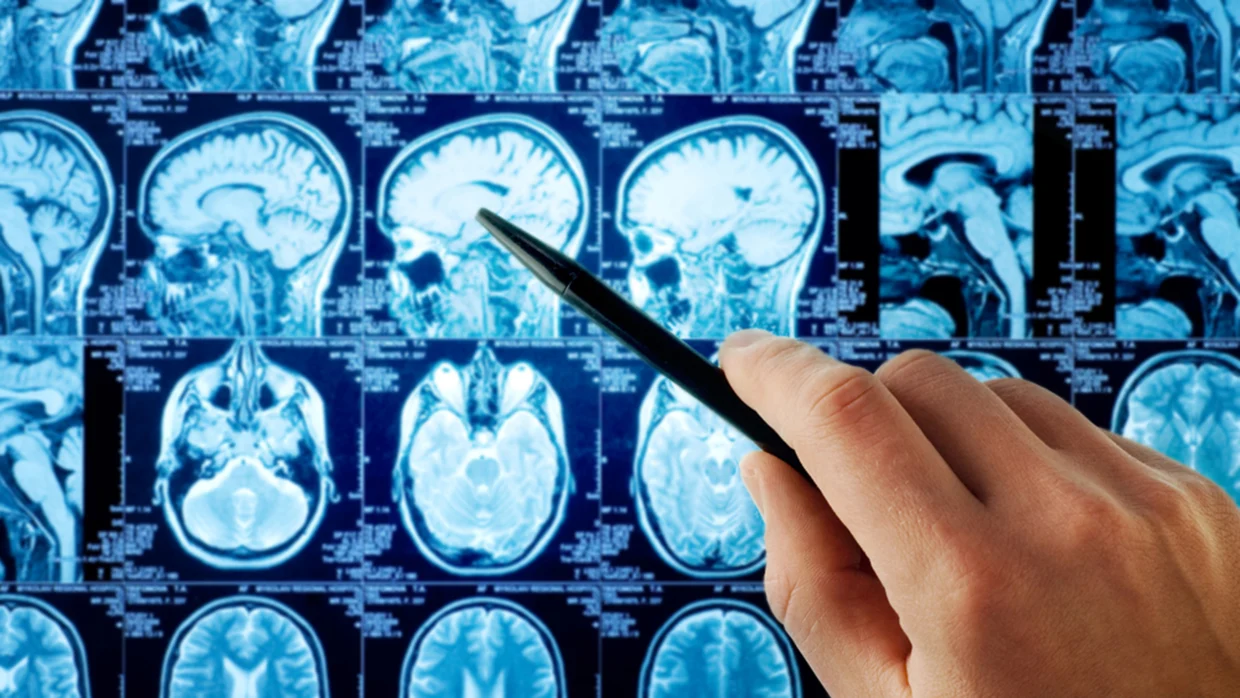
A meningioma (pronounced men-in-gee-oh-ma) is a tumour that grows in the set of 3 membranes just inside the skull, called the meninges. The function of these membranes is to cover and protect the brain and spinal cord.
Most meningiomas grow very slowly, often over many years without causing symptoms. But sometimes, their effects on nearby brain tissue, nerves or vessels may cause serious disability.
Meningiomas occur more commonly in women and are often discovered at older ages, but they may occur at any age.
Because most meningiomas grow slowly, often without any significant signs and symptoms, they do not always require immediate treatment and may be monitored over time.
Meningiomas can be grades 1, 2 or 3, but there are no grade 4 meningiomas. Within these grades, there are also different types of meningioma, which you may hear during your diagnosis or during consultations with your healthcare team.
Meningiomas are usually:
- low grade tumours
- slow growing
- unlikely to spread.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of a meningioma typically begin gradually and may be very subtle at first. Depending on where in the brain or, rarely, spine the tumor is situated, signs and symptoms may include:
- Changes in vision, such as seeing double or blurriness
- Headaches, especially those that are worse in the morning
- Hearing loss or ringing in the ears
- Memory loss
- Loss of smell
- Seizures
- Weakness in your arms or legs
- Language difficulty