What is Epilepsy?
Epilepsy is a chronic non-communicable disease of the brain that affects around 50 million people worldwide. It is characterized by recurrent seizures, which are brief episodes of involuntary movement that may involve a part of the body (partial) or the entire body (generalized) and are sometimes accompanied by loss of consciousness and control of bowel or bladder function.
Seizure episodes are a result of excessive electrical discharges in a group of brain cells. Different parts of the brain can be the site of such discharges. Seizures can vary from the briefest lapses of attention or muscle jerks to severe and prolonged convulsions. Seizure
Causes, Triggers, Risk factors, Diagnosis
Causes:
- Genetic predisposition and family history
- Head and brain injuries or trauma
- Developmental disorders
- Infectious diseases
- Prolonged febrile conditions due to serious illness
- Neurological disorders
- Cardiovascular illness
Risk factors:
Children:
1. Premature birth
2. Low birth weight
3. Congenital brain anomalies
4. Trauma like lack of oxygen at the time of birth
5. High fever and prolonged infections or illness
6. Seizures during the initial months of a child
7. Family history
8. Improper and insufficient food intake
9. Menta disabilities
10. Maternal drug/alcohol abuse
Adults:
1. Bleeding and/or abnormal blood vessel pattern in the brain
2. Brain injuries, hypoxemia, brain tumors, brain infections etc
3. Stroke, blocked arteries, and other cardiovascular illness
4. Dementia and other neurological conditions
5. Sleep deprivation
6. Alcohol/drug abuse 7. Increased stress
8. Improper food habits
9. Mental disabilities
Triggers:
- Fever
- Lack of sleep
- Stress, anxiety, worry
- Bright flashing lights
- Certain medicines or drugs
- Caffeine or alcohol
- Improper eating habits
Symptoms, types, complications
General symptoms includes motor and non-motorn symptoms and are particular to seizure type.
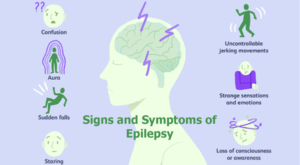
- Starry spells
- Blackouts
- Confusion
- Jerking movements of arms, legs or body (rhythmic clonic movements)
- Weak atonic muscles
- Epileptic spasms
- Twitching eyes or facial muscles
- Loss of consciousness
- Convulsions
- Loss of memory
- Temporary unresponsiveness
- Sudden rigidity, stiffness or falling
- Fear, panic, anxiety
- Change in perception of smell, taste
- Decreased vision and hearing
Types of seizures:
- Generalized Onset Seizures
- Tonic seizure
- Clonic seizures
- Absence seizures
- Atonic seizures
- Myoclonic
- Tonic-clonic seizures
- Focal Onset Seizures
- Aware seizures
- Unaware seizures
- Unknown Onset Seizures
Complications:
- Falling and accidents
- Loss of consciousness
- Status epilepticus
- Drowning
- Permanent neurological damage
- Sudden unexplained death
- Developmental delays
- Complications and side effects due to prolonged usage of anti-epileptic drugs
- Sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP)